Databricks CI/CD Methods - A Comprehensive Guide
January 15, 2024 in Data Platforms4 minutes
Explore the seamless integration of Databricks notebooks with CI/CD pipelines using GitHub Actions and Azure DevOps, complete with expert insights.
Overview
Hey there! Let’s talk about deploying Databricks notebooks through CI/CD pipelines and GitHub Actions or Azure DevOps. There are multiple methods available to deploy Databricks notebooks and jobs. We’ll cover some of these methods, along with their pros and cons. We’ll also provide our recommendation on the best method to deploy Databricks notebooks.
Methods
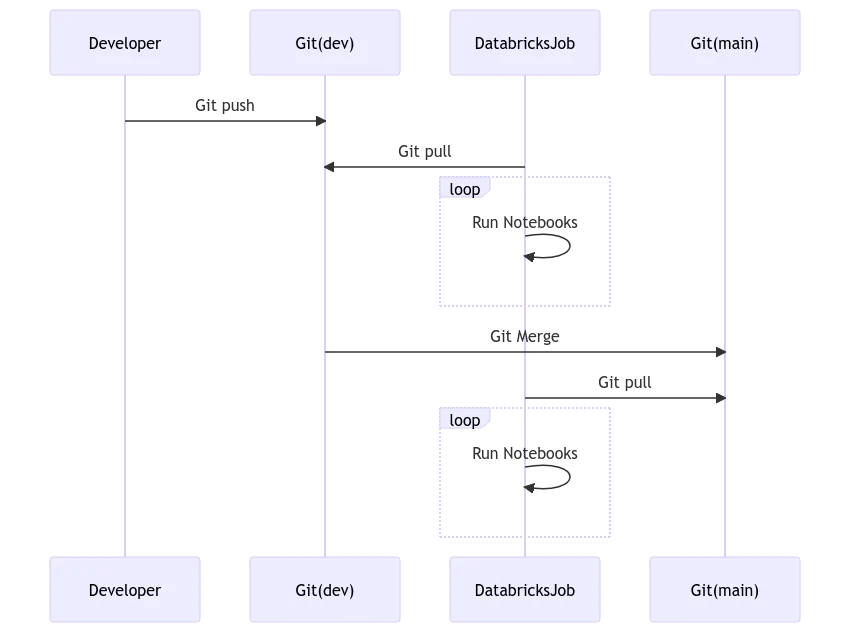
1. Using GitHub/Azure DevOps Repo Pull (Recommended)
The first method we recommend is using GitHub/Azure DevOps repo pull. It’s the simplest and cleanest method of all. In this method, we’ll create a Databricks job that will pull the notebooks from the GitHub/Azure DevOps repo and run them. There are no additional CI/CD setups required to achieve this, and all the touchpoints such as the git repo, workspace, and notebooks are isolated. There is no complex token management required either.
Databricks Jobs API accepts git_source as an argument where you can pass the repo URL, branch/tag, etc. The job will then pull the notebooks from the git repo and run them. Refer to the Databricks Jobs API documentation for more details.
Databricks Workflows, Prefect, and Airflow also support the repo pull method. However, it’s important to note that repo pull heavily relies on the availability of the git provider (GitHub/Azure DevOps). If the git provider is down, then the Databricks jobs will fail. Let’s assume a GIT token expires, or the organizational policy resets system accounts token, pretty much all jobs that rely on the git token will fail.
Pros
- Simple and no additional CI/CD setup required.
- No complex credential management required.
- All the touchpoints are isolated.
Cons
- Collaboration is difficult as all developers work in silos within their own branch.
- Code review can be difficult as most reviews happen in GitHub and not in Databricks Workspace.
- Downtime of GitHub/Azure DevOps will impact Databricks jobs.
Dependencies
- The actor who is deploying the notebooks (typically Azure Service Principal) needs to set up a git token in the Databricks workspace.
2. Using Repos API
Databricks offers the Repos API to manage the notebooks in the workspace. We can also use this API to pull the notebooks from git as part of the CI/CD pipeline and sync it with Databricks Repos. Refer to the Databricks Repos API documentation or Databricks Repos for more details.
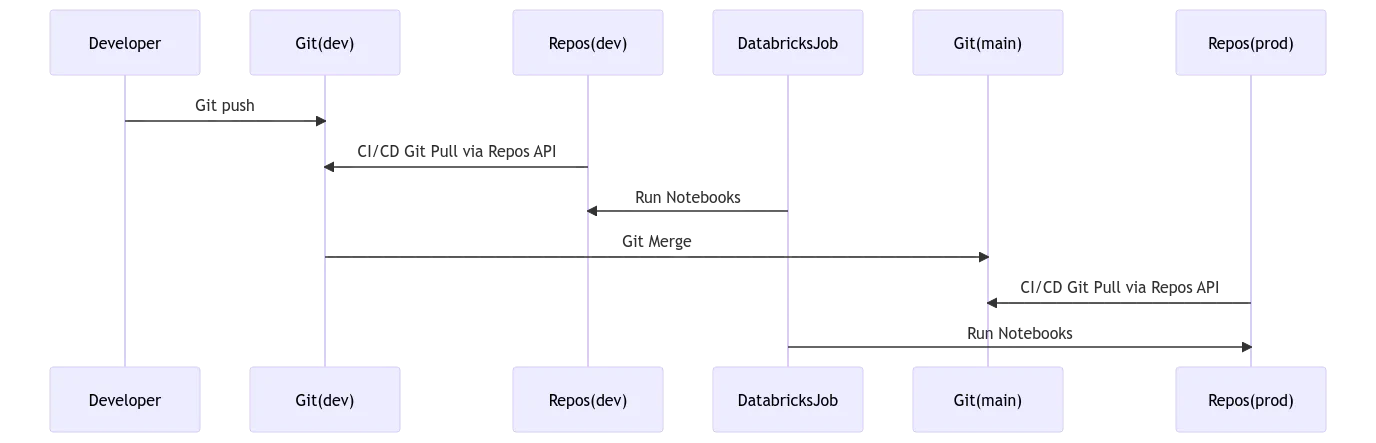
If you are interested in this method, here is my template repo that you can use to get started.
Pros
- Collaboration is easy as all developers’ work is available in the workspace under Repos.
- Code review is easy as all the reviews/results can happen in the workspace.
Cons
- Additional CI/CD setup required to pull the notebooks from git.
- Anyone having manage access can alter the notebooks in the workspace. Access control needs to be governed properly.
- Switching between release branches is difficult as you will have to create separate repos for each release.
- Adding more notebooks to the workspace counts towards the storage limit of the workspace.
Dependencies
- The actor who is deploying the notebooks (typically Azure Service Principal) needs to set up a git token in the Databricks workspace.
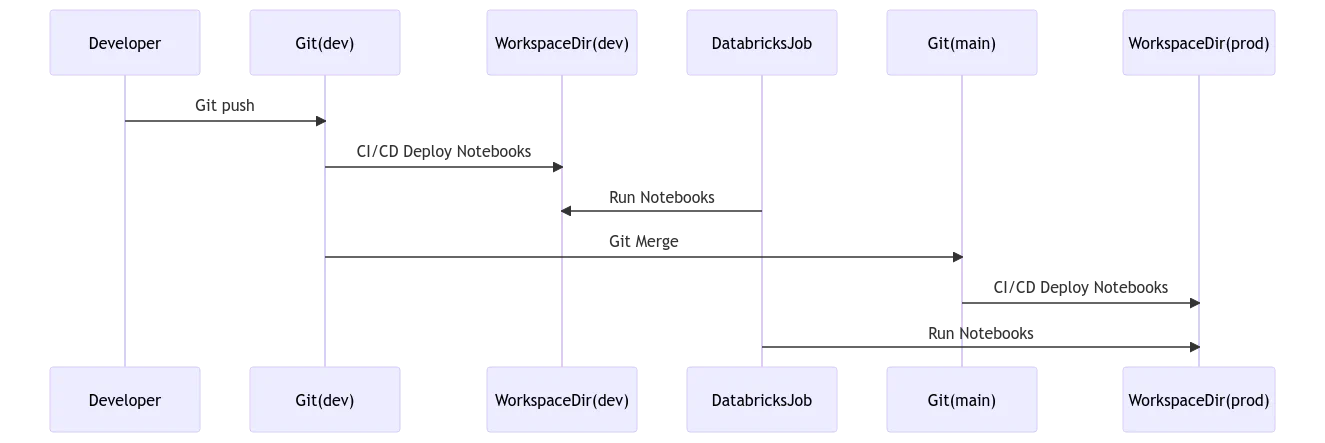
3. Using Workspace API
This is a traditional way of CI/CD where you import notebooks from the git repo to the workspace and create folders under the workspace directory. You can then create a Databricks job to run the notebooks from the workspace directory. This is the least recommended method.
Pros
- Collaboration is easy as all developers’ work is available in the workspace under Repos.
Cons
- Additional CI/CD setup required to pull the notebooks from git.
- Anyone having manage access can alter the notebooks in the workspace. Access control needs to be governed properly.
- Folders and notebooks could eventually grow and become unmanageable. It’s possible that you end up importing too many release folders or notebooks can become stale.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the first method provides the most straightforward and efficient approach to deploy Databricks notebooks through CI/CD pipelines. We recommend considering the pros and cons of each method and selecting the one that aligns best with your team’s specific needs and requirements. By adopting this recommended approach, you can ensure a seamless and streamlined deployment process for your Databricks notebooks.
While other methods like using Repos API and Workspace API offer their own advantages, such as enhanced collaboration and easy code review, they come with additional complexities and potential drawbacks, such as managing access control and storage limitations. Ultimately, the decision is up to you and your team to determine which method is best suited for your specific needs and requirements.